In the modern world, we are exposed to different securities breaches and have to forego our privacy in exchange for digital platform services. The transparency of blockchains provides users with a sense of security, but it’s still not enough. In this case, Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP) comes as the perfect method to provide privacy guarantees.
1. What is Zero-Knowledge Proof?
Zero-knowledge proof is a method for a party to prove that they possess knowledge about a piece of information without disclosing the actual information.
It first appeared in a 1985 MIT paper “The knowledge complexity of interactive proof systems”. In this paper, Shafi Goldwasser and Silvio Micali show the possibility of a “prover” to convince a “verifier” that a statement about a data point is true without revealing any additional information about the data. The prover tries to prove a claim, while the verifier takes responsibility to validate the claim.
Zero-knowledge proof can be interactive, where the prover convinces an individual verifier and needs to repeat the process for each different one, or non - interactive, where the prover shows proof that can be used and verified by anyone.
Zero-knowledge proofs
2. The benefits of Zero-Knowledge Proof
The primary benefit of zero-knowledge proof is to leverage privacy within transparent systems like public blockchain networks. Users using blockchains can see and download all data on the ledger, which makes blockchains to be highly transparent. Zero-knowledge proof adds to this benefit by enabling the execution of smart contracts without revealing private data.
Traditional institutions such as enterprises, companies, or banks need to ensure privacy within their blockchain networks due to competition, trade secrets, and law requirements. They are required to safeguard their clients' information according to various regulations like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Zero-knowledge proof now opens up a wide range of use cases for institutions to interact with public blockchain networks but still keep their sensitive data safe and under control.
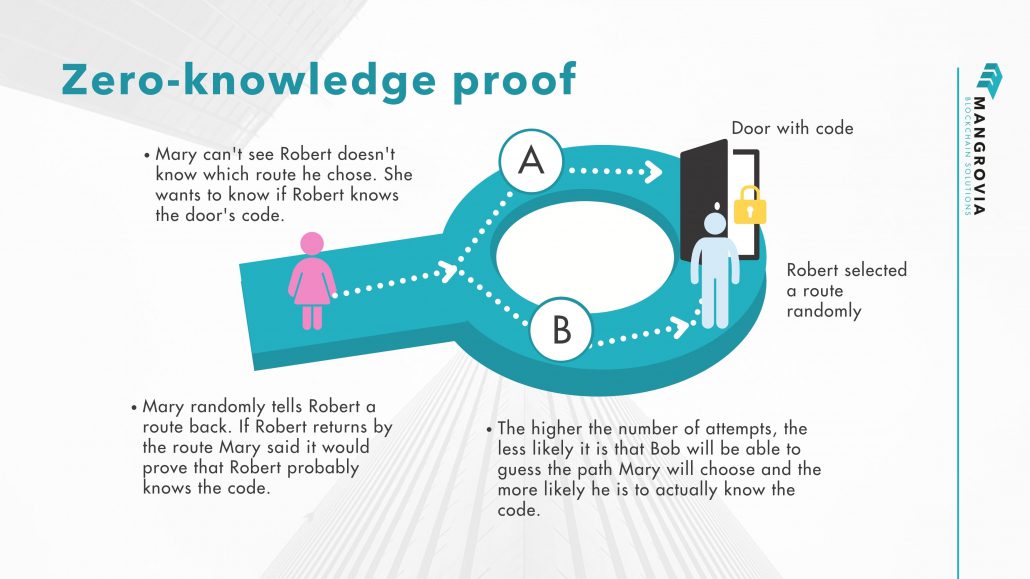
Zero-knowledge proof intuitive example
3. Use case of Zero-Knowledge Proof
a. Anonymous Payment
Credit card payments are visible to multiple parties like banks, payment providers, and government authorities to limit and identify illegal activities, however, this sometimes violates the privacy of ordinary citizens. Cryptocurrencies are created as a means to conduct private transactions but due to the nature of blockchain, most cryptocurrency transactions are still visible on the public blockchain.
There is some privacy-focused blockchain, like Monero and ZCash, that protect transaction details, including sender and receiver addresses, asset, quantity, and timeline. This is made possible by implementing zero-knowledge proof technology into the blockchain protocol: they allow nodes to validate the transaction without knowing the transaction data.
b. Identity protection
As current identity management leaves room for information leaks, zero-knowledge proofs can help users validate identity without revealing sensitive details. For example, users can prove their citizenship without providing ID or passport details.
c. Authentication
Users are required to provide their identity to be given access to online services. They need to provide personal information like names, email addresses, birthdays, etc. Zero-knowledge proof can help authenticate both the platforms and users. With the proof users have obtained, they can use it to authenticate their identity to use the services. This will improve customer experience and help organizations free from the need to store large amounts of information.
d. Others
Zero-knowledge proof is able to provide many other use cases, such as storage protection, data sharing, encrypted messaging, file system protection, and many more. All the use cases utilize the privacy-focused nature of the technology to improve current online services and experiences.
4. Challenge and Conclusion
Zero-knowledge proof has improved over the years and is used in different meaningful use cases. However, the drawbacks of this technology are visible and require improvements. Notable is the hardware costs, as generating zero-knowledge proofs involves complex calculations on expensive specialized machines. This can increase the cost for both the organizations and end-users. The proof verification costs now come as a challenge for users, with the increased gas fee to complete the process.
With many challenges to take into account, zero-knowledge proof is undeniably an important and promising technology to be implemented in the blockchain. Blockchain can now be the super protective platform everyone hoped for, and time will tell.



























